Iron Deficiency: Symptoms, Causes & What to Eat

Iron Deficiency and Fatigue: How to Recognize Symptoms and What Really Helps
Always tired, exhausted, or pale, even though you’re getting enough sleep and eating healthily? Many people experience these issues regularly. Often, quick explanations are given: too much stress, not enough coffee, or changes in the weather. But what’s often overlooked is that your body is sending clear warning signals and iron deficiency is frequently the root cause. To dive deeper into why blood tests are essential for your health, check out our blog: “Why blood tests are important for your health | Early detection with G24.”
Iron deficiency is one of the most common deficiencies worldwide, especially among women, children, vegetarians, and people with increased needs. The good news? It can be easily diagnosed and effectively treated.
In this article, you’ll get to know why iron is so important for your body, which symptoms can indicate a deficiency, what blood values matter, and how you can improve your iron levels through nutrition, testing, and proper action.
What Is Iron Deficiency?
Iron deficiency occurs when your body lacks enough iron over a long period to maintain essential functions. Although iron is only present in small amounts in the body, it’s essential for processes like blood formation, oxygen transport, and energy metabolism. If left undetected or untreated, it can lead to iron deficiency anemia, a more severe form with serious symptoms.
The Role of Ferritin and Iron in the Body
Iron levels in blood tests aren’t measured as just “iron”, they appear in different forms. One key indicator is ferritin, the protein that stores iron. Unlike serum iron, which fluctuates based on diet and time of day, ferritin offers a stable reflection of your body’s iron stores.
Low ferritin levels don’t just affect oxygen delivery, but also your immune system, muscles, and mental performance. Women on their period, athletes, pregnant individuals, and people with chronic conditions are especially at risk.
Iron Deficiency Is Not the Same as Anemia
Many people assume iron deficiency and anemia are the same, but that’s not true. Iron deficiency is the precursor, while anemia is the result of prolonged deficiency. Anemia only develops once the deficiency has progressed far enough to reduce hemoglobin concentration in the blood.
You may already suffer from clear signs of iron deficiency even if your hemoglobin levels appear normal. This early phase is where preventive blood testing, like Ferritin Test offered by G24, becomes critical.

How to Recognize Iron Deficiency in Daily Life
Iron deficiency often develops gradually, making it hard to notice. The symptoms are often vague and easily attributed to other causes. Typical signs that may indicate iron deficiency:
- Constant tiredness despite getting enough sleep
- Fatigue and weakness
- Dizziness, brain fog, headaches
- Pale skin, dark under-eye circles, brittle nails
- Hair loss
These symptoms don’t have to appear all at once. Even small changes you can’t quite explain may be an early warning sign and especially if you belong to a risk group.
A simple blood test with G24 focused on ferritin often provides more clarity than months or years of guessing.
Why Low Ferritin Causes Fatigue
Iron is essential for energy production. When ferritin is low, the body lacks the raw materials to produce hemoglobin, which transports oxygen. That means your cells get less oxygen and you feel constantly tired, even if you sleep well and eat right.
Often, those who are affected try to compensate with coffee or supplements, but without testing, the cause remains unclear. A simple ferritin test with G24 can give clarity and help prevent worse symptoms. Hence, Book your appointment now.
Ferritin and Iron Levels in the Blood – What They Mean
Ferritin is a blood protein that reflects your iron storage. Low ferritin means your iron stores are nearly depleted, even if your hemoglobin level is still within the normal range and symptoms may show up early.
On the other hand, High ferritin can signal chronic inflammation, liver disease, or iron overload. In such cases, a more detailed assessment is useful, because an “elevated ferritin” result doesn’t always mean excess iron, it can also reflect ongoing inflammation in the body.
Reference ranges for orientation:
- Normal ferritin level for women: approx. 15–150 ng/ml
- Men: 30–300 ng/ml
However, these reference ranges can vary based on age and health status. That’s why it’s important to interpret the results in context, ideally together with additional markers like serum iron, transferrin saturation, and CRP level.
Why Women Are Particularly Affected
Due to biological factors, women are especially prone to iron deficiency. They often need higher levels and should aim for ferritin of at least 30–50 ng/ml.
Causes of Iron Deficiency and Fatigue
Iron deficiency often arises from a combination of factors that gradually throw the body off balance. The deficiency is frequently hidden behind symptoms like tiredness, difficulty concentrating, or general fatigue, symptoms that are easily attributed to stress or daily life.
One common reason for low iron levels is an unbalanced diet. People who primarily eat plant-based foods often absorb less bioavailable iron. That’s because the iron in plant-based foods (called non-heme iron) is absorbed by the body far less efficiently than iron from animal sources. Dieting, one-sided eating habits, or chronically irregular meals can also lead to insufficient iron intake over time.
Additionally, certain foods can inhibit iron absorption for example, coffee, black tea, or dairy products, especially when consumed at the same time as iron-rich meals. At the same time, supportive nutrients like vitamin C, which can significantly improve iron absorption.
If you regularly consume too little iron through your diet, you may not be replenishing your body’s stores adequately, especially if your iron needs are elevated.
Causes in Women – Menstruation and Pregnancy
Women are particularly often affected by iron deficiency, and this is mainly due to blood loss during every menstrual cycle. The heavier or longer the bleeding, the greater the loss. Especially in the case of very heavy periods, this can lead to a gradual depletion of the body’s iron stores over time.
During pregnancy, the body’s iron requirements increase significantly, as both the growing baby and the placenta need to be supplied. If this increased need is not met, a deficiency can quickly develop with consequences such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and a weakened immune system. After childbirth, breastfeeding, hormonal changes, and disrupted sleep patterns can put further strain on iron balance.
In addition to diet and blood loss, there are other factors that can lead to iron deficiency. Chronic conditions such as intestinal inflammation (e.g. Crohn’s disease, celiac disease) or other gastrointestinal disorders, or certain medications can block iron absorption in the body. That’s why regular testing is crucial to find the cause and fix it.
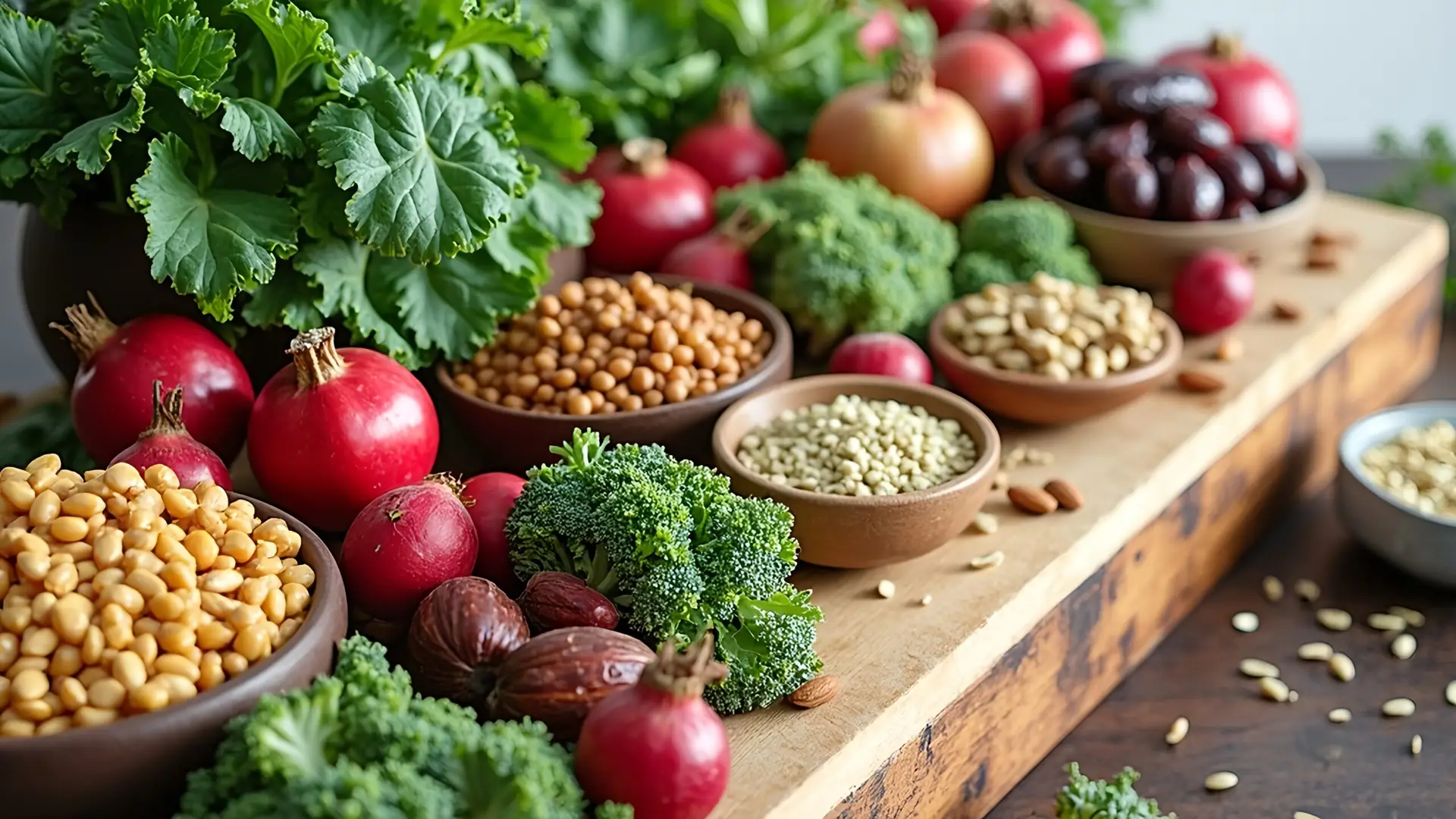

Iron-Rich Diet: What You Should Eat
Iron content and absorption vary across foods. Best absorbed is heme iron from animal sources. Plant-based iron is harder to absorb.
Iron-rich animal-based foods:
- Red meat (beef, lamb)
- Liver
- Blood sausage
- Egg yolk
- Fish and seafood (e.g. mussels)
Iron-rich plant-based foods:
- Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, beans
- Whole grains (e.g. oats, quinoa, millet)
- Nuts and seeds (especially pumpkin seeds, sesame)
- Leafy greens (e.g. spinach, chard)
- Beets
A balanced combination of both sources can help cover your daily iron needs well.
Tips:
- Pair iron with vitamin C (e.g., citrus, bell peppers) to improve absorption.
- Avoid coffee, tea, and dairy with iron-rich meals, they block absorption.
You should consult a doctor if your ferritin level remains consistently low despite dietary changes, or if you experience severe weakness, concentration problems, or worsening symptoms. Early diagnosis can help prevent complications.
Conclusion | When to Take Action
Iron deficiency is a silent condition that often goes unnoticed for a long time. Yet, it’s one of the most common causes of fatigue, poor concentration, and a weakened immune system. If your iron levels are in check but you still experience ongoing fatigue or immune issues, it’s worth exploring other causes like hidden inflammation. Read our blog “CRP and Inflammatory Blood Markers | Causes, Symptoms & Treatment” to understand how CRP levels can reveal more about your overall health.
The good news is, once you know what to look for, you can take targeted steps to address it quickly. The good news is, once you know what to look for, you can take targeted steps to address it quickly.
Key points:
- Symptoms such as constant fatigue, hair loss, dizziness, or sensitivity to cold may indicate low ferritin levels, even if your hemoglobin level is still within the normal range.
- Get your iron and ferritin tested.
- Nutrition, targeted supplements, and medical support can help you replenish your iron stores.
With G24, it’s fast and simple to get tested in a partner pharmacy or from home. You’ll receive a clear report and, if desired, personalized recommendations.
G24 makes it easy for you to do just that, simple, fast, and transparent. With just a few clicks, you can book your blood test at a partner pharmacy near you. You’ll receive a clear report within 24-48 hours and if desired, personalized recommendations for nutrition and supplementation.
Health is not a guess – it’s measurable, manageable, and actionable.
Beliebte Blogs
Test for you
FAQ
We always strive to keep our customers happy and informed!
Why am I constantly tired, even though I sleep enough?
Persistent tiredness despite adequate sleep may indicate iron deficiency, especially with symptoms like dizziness, brain fog, or pale skin. Iron is vital for oxygen transport, and low ferritin levels can impair oxygen delivery to cells, causing fatigue. A simple ferritin blood test can offer clarity.
What helps against persistent fatigue caused by iron deficiency?
Improving iron levels through a combination of nutrition and lifestyle changes can significantly boost your energy. Include iron-rich foods (like red meat, lentils, spinach), combine them with vitamin C, and avoid inhibitors like caffeine. If levels are severely low, supplements or medical guidance may be needed. Testing with G24 helps monitor your recovery.
How long does it take to correct iron deficiency?
Mild iron deficiency can improve within a few weeks with dietary changes and supplements. However, restoring ferritin levels to normal may take 2 to 3 months or longer, depending on severity. Re-testing is recommended after 6 to 8 weeks to assess progress.
What does it mean if my ferritin level is too low or too high?
Low Ferritin: Indicates depleted iron stores and is often the first sign of iron deficiency before anemia develops.
High Ferritin: Can indicate inflammation, liver conditions, or iron overload. It’s important to evaluate it alongside CRP (inflammatory marker) and other values.
Can iron deficiency cause headaches, dizziness, or nausea
- Yes. Iron deficiency affects oxygen delivery to the brain and muscles, which can lead to:
Headaches, Dizziness, Fatigue, Muscle weakness and in some cases, even nausea or brain fog.
If you experience these symptoms regularly, it’s worth getting your iron and ferritin levels tested